With the advancement of society, the fourth industrial revolution has brought rapid technological innovation to various sectors, including the food industry. In recent years, microwave technology has been successfully applied to the thawing of meat products, offering significant benefits over traditional methods.
1. What is Microwave?
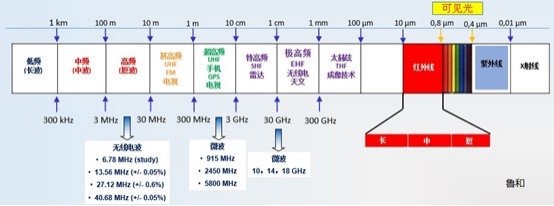
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from 1 mm to 1 m (frequencies of 300 MHz to 300 GHz). Due to their ability to penetrate, reflect, and absorb, microwaves have become widely used in food processing for heating, drying, sterilizing, and thawing.
2. Principles of Microwave Thawing
Common industrial thawing methods for frozen meat include natural air thawing, water thawing, and steam-assisted thawing at low temperatures and high humidity. However, these methods rely on heat conduction from the outside to the inside, resulting in uneven thawing, potential microbial growth, and significant loss of meat juice and protein. In contrast, microwave thawing uses 915 MHz electromagnetic waves, which cause polar molecules in the meat (especially water molecules) to oscillate, producing internal frictional heat and warming the meat uniformly without a temperature gradient.
Since microwaves decay upon entry, penetration depth varies with frequency. For example, 915 MHz microwaves penetrate about 33.3 cm in air. Microwaves pass through plastic, glass, and ceramics without being absorbed, whereas they cause foods and water to heat up and reflect off metals.
3. Structure of a Microwave Thawing Machine
Microwave thawing machines come in batch and continuous types. Regardless of type, each machine typically consists of a microwave chamber, microwave generator, waveguide, magnetron, cooling system, conveyor, and control system.

4. Advantages of Microwave Thawing
Microwave thawing technology offers many unique advantages for food processing:
- Fast Thawing with High Output: A standard 25 kg frozen meat block at -18°C can be thawed to -3°C within 3–10 minutes, allowing rapid preparation of raw materials for production.
- Space-Saving and Energy-Efficient: These systems feature high-tech components with energy efficiency up to 85%. The compact design requires less space and minimizes floor area requirements.
- Uniform Temperature Control: For evenly distributed fatty and lean meat, microwave thawing ensures a consistent temperature throughout, with internal and surface temperatures nearly identical, precise to +/-1°C.
- No Juice Loss, Zero Thawing Loss: Unlike conventional methods that result in up to 8% thawing loss, microwave thawing preserves all meat juices, retaining high protein content and yielding a high-quality product with no wastage.
- Simple Operation and Safety: Batch microwave thawing requires only one operator, while continuous systems are tunnel-structured for automated, seamless integration with upstream and downstream processes. Advanced designs prevent microwave leakage and ensure safe operations.
- Hygienic, Clean, and Free from Cross-Contamination: The short thawing time eliminates microbial growth, and the machine's design follows strict food hygiene standards, preventing cross-contamination and ensuring a sanitary environment.
- Broad Application Scope: Microwave thawing is versatile, suitable for various frozen meats (pork, beef, poultry, lamb), seafood, fruits, vegetables, and dough products.
In conclusion, the application of microwave thawing in meat processing offers even temperatures, zero juice loss, and no microbial growth or wastewater, ensuring optimal product quality and safe processing for downstream production stages.